Fona
- unexpecteddinolesson
- Jul 18, 2024
- 3 min read
MEANING: The origin
PERIOD: Late Cretaceous
CONTINENT: North America
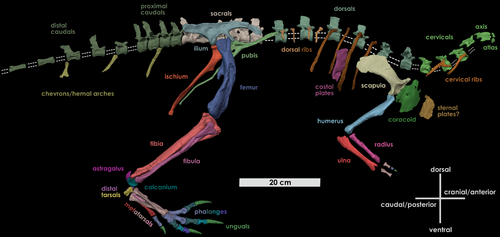
Fona is a basal ornithopod dinosaur that lived about 99 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous of what is now North America. It was a small bipedal herbivore, measuring about 2.5 m in length, with a good portion of this length in its tail. Multiple individuals have been discovered, thanks to their exceptional preservation, as though they were already buried before they died. This, as well as the proportions of their limbs, indicate that Fona was likely a burrower, spending much of its life underground.

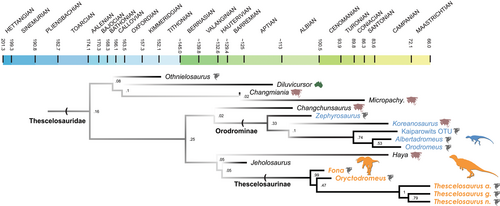
Abstract from paper: Thescelosaurines are a group of early diverging, ornithischian dinosaurs notable for their conservative bauplans and mosaic of primitive features. Although abundant within the latest Cretaceous ecosystems of North America, their record is poor to absent in earlier assemblages, leaving a large gap in our understanding of their evolution, origins, and ecological roles. Here we report a new small bodied thescelosaurine—Fona herzogae gen. et sp. nov.—from the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah, USA. Fona herzogae is represented by multiple individuals, representing one of the most comprehensive skeletal assemblages of a small bodied, early diverging ornithischian described from North America to date. Phylogenetic analysis recovers Fona as the earliest member of Thescelosaurinae, minimally containing Oryctodromeus, and all three species of Thescelosaurus, revealing the clade was well-established in North America by as early as the Cenomanian, and distinct from, yet continental cohabitants with, their sister clade, Orodrominae. To date, orodromines and thescelosaurines have not been found together within a single North American ecosystem, suggesting different habitat preferences or competitive exclusion. Osteological observations reveal extensive intraspecific variation across cranial and postcranial elements, and a number of anatomical similarities with Oryctodromeus, suggesting a shared semi-fossorial lifestyle.
Fona is from the Cretaceous. The Cretaceous is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago. It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin creta, "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period.
The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct flora and fauna, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth by the end of the Cretaceous, coincident with the decline and extinction of previously widespread gymnosperm groups.
The Cretaceous (along with the Mesozoic) ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, a large mass extinction in which many groups, including non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and large marine reptiles, died out. The end of the Cretaceous is defined by the abrupt Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K–Pg boundary), a geologic signature associated with the mass extinction that lies between the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras.
Fona is an ornithopod. Ornithopoda is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous. They dominated the North American continent, then spread to Asia and eventually the southern hemisphere toward the end of the Cretaceous. Their major evolutionary advantage was their batteries of teeth, which allowed them to process vegetation in an extremely efficient way. Ornithopods were a diverse group, and included the hadrosaurs, which continued to dominate until the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which wiped out all non-avian dinosaurs.